Plastic Fuel
In the quest to combat environmental degradation and pivot towards sustainability, innovative solutions are emerging at the intersection of technology and ecology. One of the most promising frontiers in this battle is the development of fuels created from plastic waste. This revolution promises to address the burgeoning crisis of plastic pollution and significantly reduce our carbon footprint, marking a pivotal shift in our approach to energy consumption and waste management. Efforts are being led by public institutions like Swansea University, the University of California, Irvine, and Penn State and private companies like Skyrora, Plastic2Oil, Neste/Alterra Energy, and Paterson Energy.
Skyrora’s Leap with Ecosene
At the forefront of this innovation is Skyrora, a UK-based aerospace company that has developed Ecosene, a fuel derived from waste plastics. Ecosene, designed to minimize the environmental impact of rocket launches, reflects Skyrora’s commitment to sustainability. By converting non-recyclable plastics into a high-grade kerosene substitute, Skyrora addresses both space industry demands for propulsion and global environmental concerns regarding plastic waste and carbon emissions.

Credit – skyrora.com
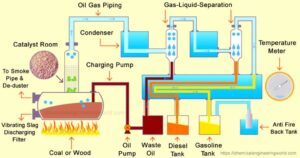
Development of Ecosene
Skyrora’s Ecosene undergoes a two-step conversion process, transforming plastics previously destined for landfills into usable fuel. This process not only offers a solution to the problem of plastic waste but also provides an eco-friendly alternative to traditional rocket fuels. Ecosene is comparable to RP-1 rocket fuel but boasts a 45% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Its properties are particularly beneficial for launch sites in Scotland, where weather can be unpredictable, as Ecosene does not require cryogenic freezing and can be stored for extended periods. (“Skyrora tested innovative environmentally friendly fuel Ecosene | Skyrora,” 2020)
Environmental Impact
The motivation behind Ecosene stems from a larger environmental conscience. The UK faces significant challenges with plastic waste, with only 46.2% of plastics being recycled as of 2019 and a substantial amount ending up in landfills or the ocean. Skyrora’s initiative not only mitigates the waste problem but also aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals by enabling cleaner launches of Earth observation satellites. These satellites are crucial for monitoring environmental changes and advancing global sustainability efforts. (“Ecosene and waste plastics | Skyrora,” 2022)
Testing and Implementation
Skyrora has conducted extensive testing of Ecosene, including multiple 30-second test firings to assess its performance compared to traditional kerosene. These tests, crucial for validating Ecosene’s efficacy and environmental benefits, have paved the way for its use in Skyrora’s XL launch vehicle. The XL, a three-stage, light-class launcher, is designed to deliver small satellites into sun-synchronous and polar orbits and will utilize Ecosene for its first and second stages. (“COP26 – a space with no borders | Skyrora,” 2021)
Contribution to Climate Goals
Skyrora’s development of Ecosene and its broader commitment to sustainability underscore the vital role of space technology in addressing climate change. Earth observation satellites, enabled by eco-friendly launch solutions like Ecosene, provide indispensable data for climate research and environmental monitoring. This data is crucial for informing global efforts to combat climate change, highlighting the interconnection between space exploration and environmental stewardship. (“COP26 – a space with no borders | Skyrora“)
The Global Movement Towards Sustainable Fuel Alternatives
Skyrora’s innovative use of Ecosene, a fuel derived from plastic waste, is part of a broader movement towards sustainable fuel alternatives across various industries. Several other public institutions and private companies are also exploring technologies to convert plastic waste into fuel, demonstrating a global commitment to tackling plastic pollution and creating cleaner energy sources.
Swansea University and University of California, Irvine: Researchers have developed methods to convert plastic waste into hydrogen fuel and diesel. Swansea University’s approach uses a photocatalyst to break down plastic in sunlight, producing hydrogen gas, which could potentially power cars in the future. Meanwhile, chemists from the University of California, Irvine, have found a way to dissolve the bonds of polyethylene plastic to create petroleum and other fuel products, using less heat and resulting in a liquid fuel that can be used for various industrial purposes. (Evans, 2023)
Penn State: Researchers have developed a more efficient method for converting hard-to-recycle plastic waste into fuel. Their process involves a catalytic method that degrades polypropylene, a type of plastic commonly found in toys, medical devices, and car parts, into fuel. This advancement holds promise for addressing the dual challenges of plastic waste accumulation and the search for alternative energy sources. By refining this technology, Penn State aims to contribute significantly to sustainable waste management and fuel production practices. (Carroll, 2022)
Plastic2Oil: A US firm that transforms waste plastic into ultra-low sulphur diesel. Their technology processes unwashed, unsorted plastic, creating cleaner burning fuel compared to traditional sources due to its low sulphur content. This process is particularly beneficial for developing nations that commonly use sulphur-heavy diesel. (Evans)
Neste and Alterra Energy: Neste, a leading provider of renewable diesel, has partnered with Alterra Energy to commercialize Alterra’s waste plastic liquefaction technology in Europe. Alterra’s technology turns a broad range of plastic waste into a material similar to crude oil, which can then be processed into high-quality feedstock for polymers and chemicals. This collaboration aims to accelerate the adoption of chemical recycling and develop capacity to transform hard-to-recycle plastic waste into valuable products. (Sieppi, 2021)
Paterson Energy: Based in Chennai, India, this company has developed a technology to convert plastic waste into fuel. Their process, known as thermo-chemical depolymerization, involves decomposing plastic materials at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. The resulting product is a pyro oil (biocrude) that can be used as an alternative to conventional fuels in various industrial applications. Paterson Energy’s technology represents a sustainable waste-to-energy solution, capable of handling most kinds of plastic waste, including single-use plastics (Karelia, 2024).
Implications for the Climate Crisis
The development and utilization of fuels from plastic waste hold profound implications for addressing the climate crisis. These innovative solutions not only offer a way to reduce plastic pollution, which clogs our oceans and landscapes, but also present an opportunity to decrease reliance on fossil fuels. By repurposing plastic waste into fuel, these initiatives contribute to the circular economy, enhancing resource efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, the widespread adoption of such technologies could significantly mitigate the environmental impact of both the energy and waste management sectors, providing a double-edged sword against climate change.
In conclusion, the pioneering work of companies like Skyrora, along with other global efforts to develop sustainable fuel alternatives from plastic waste, marks a critical step forward in our journey towards a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future. As these technologies mature and become more widely adopted, they promise to play a crucial role in solving some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time, paving the way for a cleaner, greener planet.
References
Carroll, M. (2022, September 28). Scientists improve process for turning hard-to-recycle plastic waste into fuel. The Pennsylvania State University | Penn State. https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/scientists-improve-process-turning-hard-recycle-plastic-waste-fuel/
COP26 – a space with no borders | Skyrora. (2021, July 13). Skyrora – NewSpace rocket company from the UK. https://m.skyrora.com/cop26-a-space-with-no-borders/
Ecosene and waste plastics | Skyrora. (2022, April 13). Skyrora – NewSpace rocket company from the UK. https://skyrora.com/ecosene-and-waste-plastics/
Evans, S. (2023, May 31). Turning waste into power: The plastic to fuel projects. Power Technology. https://www.power-technology.com/comment/plastic-to-fuel/
Karelia, G. (2024, February 27). Chennai couple develop new tech, turn 150 tons of plastic waste into low-cost fuel. The Better India. https://www.thebetterindia.com/200794/chennai-innovation-technology-plastic-to-fuel-alternative-low-cost-green/
Sieppi, S. (2021, January 4). Neste acquires minority stake in Alterra energy; companies partnering to commercialize Alterra’s waste plastic liquefaction technology in Europe. Neste. https://www.neste.com/news/neste-acquires-minority-stake-in-alterra-energy-companies-partnering-to-commercialize-alterra-s-waste-plastic-liquefaction-technology-in-europe
Skyrora tested innovative environmentally friendly fuel Ecosene | Skyrora. (2020, January 24). Skyrora – NewSpace rocket company from the UK. https://skyrora.com/skyrora-tested-innovative-environmentally-friendly-fuel-ecosene/